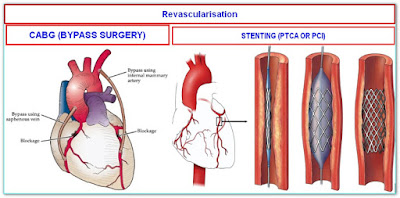
WHAT IS REVASCULARISATION?
Procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscle either by placing stent at the area of narrowing or putting a bypass graft beyond the block. This is primarily done when you have blockages in your blood vessels supplying the heart. There are two ways to revascularize.
1.CABG (Bypass surgery)
CAN MEDICATION REOPEN MY NARROWED HEART VESSELS?
Medication rarely decreases the amount of narrowing caused by the deposition of fatty material. If it all it does, it is very minimal. However, your medication slows down the process of deposition of the fat in the area of narrowing and also delays the progression of narrowing in new areas. In fact, it is the medication and healthy lifestyle that makes the development of newer deposits of fatty material
slower. In this way, they prevent future heart attacks and prolong your life. Stenting (PCI) or bypass surgery (CABG) does not have any protective effect in prevention of new blocks. Hence, you need to continue your medication even after stenting or bypass surgery without fail.
slower. In this way, they prevent future heart attacks and prolong your life. Stenting (PCI) or bypass surgery (CABG) does not have any protective effect in prevention of new blocks. Hence, you need to continue your medication even after stenting or bypass surgery without fail.
SHOULD I TAKE MEDICATION EVEN AFTER STENTING (PCI) OR BYPASS SURGERY (CABG)?
Yes. Medication and adhering to a healthy lifestyle is mandatory to every patient with blocks in the heart vessel whether he/she advised stenting or bypass surgery (CABG)
WHAT ARE THE GOALS OF STENTING IN GRADUALLY NARROWED HEART VESSELS?
The goals of stenting are
· improve your quality of life
·To make you free from symptoms such as chest pain.
·Though it has some role in preventing you from having future heart attacks and prolonging your life, medication and lifestyle changes have a predominant role in these aspects. You can still have heart attacks even after successful stenting unless you maintain
a healthy lifestyle and take prescribed medications regularly.
a healthy lifestyle and take prescribed medications regularly.
·Improve a person’s ability to exercise (exercise tolerance) – You may find that you can start to do much more than before.
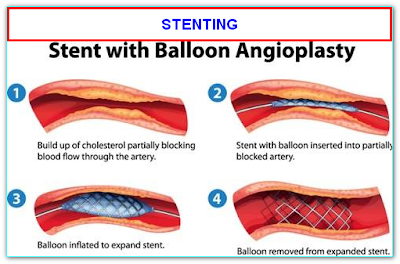
WHAT IS STENTING?
·It is also known as “percutaneous coronary intervention” or PCI or PTCA in medical terms
·It is a procedure done by a cardiologist that inserts metal stents at the site of a major blockage to open the heart vessel. In this way, it normalizes blood flow to the heart muscle and decreases your symptoms.
WHEN DO I NEED STENTING WHEN MY BLOCKS DEVELOPS GRADUALLY?
· You will experience Chest pain whenever blood flow to the heart muscle decreases due to the development of plaques. This is called “angina pectoris” (often referred to as just “angina”).
- These symptoms can be reduced with medication that either increases blood flow to the heart muscle or decreases oxygen
demand of the heart muscle. However, some people may experience persistent and intolerable chest pain despite adequate medical treatment. In these cases, revascularization by either stenting or bypassing is very helpful to improve quality of life by alleviating chest pain.
DO ALL BLOCKS NEED STENTING
·No.
The usefulness of stenting (PCI) depends upon the severity of arterial narrowing and the location of the narrowing in your heart vessels. Stenting (PCI) is often recommended when arterial narrowing is moderate to severe (more than 50-70% narrowing ) in only one or two heart vessels out of three vessels. Bypass surgery (CABG) is preferable in those with blocks in all three or four main heart vessels. Stenting (PCI) may be less effective in patients who have diabetes when compared to bypass surgery (CABG), especially if there are two or three vessels involved.
·Some patients may have narrowed in multiple locations in multiple heart vessels or may have narrowing of main heart vessel (the left main coronary artery or LMCA) that supplies blood flow to 75% of the heart muscle. These patients tend to live longer when they
have coronary artery bypass surgery rather than medical treatment alone or
stenting (PCI).
have coronary artery bypass surgery rather than medical treatment alone or
stenting (PCI).
CAN I UNDERGO STENTING AND CABG SEQUENTIALLY?
- For some patients with blockages in more than one artery, both stenting and CABG (sequentially) are used in order to achieve the best result. This is called hybrid PCI.
CAN I UNDERGO CABG IN THE FUTURE ONCE I HAVE A STENT IN MY HEART VESSEL?
- Having stents in heart vessels does not preclude one from bypass surgery in the future. Millions of patients underwent bypass after stenting and they are doing well.
WHAT TESTS WILL MY DOCTOR ADVISE BEFORE STENTING?
- Your doctor may advise basic Blood tests, ECG tests, and 2d echo tests before stenting. These tests help to ensure that other potential medical problems are identified and managed prior to the procedure. Coronary angiography is performed in all patients before stenting. Stenting can be performed at the same time of angiography (Adhoc PCI) or later.
BEFORE THE PROCEDURE
Food: avoid solid food after midnight the night before the test.
Your stenting may be canceled by the doctor if you eat after this time.
Have plenty of clear fluids only up to 3 hours before the test.
One need to shave the groin area before the test
Remove all jewelry before entering the Cath lab.
One may keep glasses, hearing aid(s), and denture(s) on during the procedure.
Inform the treating doctor if you have a known allergy to x-ray dye, iodine, shellfish, or any other allergies.
Medication (sedatives) that help you relax just before the angiogram will be given to you but you will be awake throughout the procedure.
You will also be given bolus doses of blood thinners prior to stenting that prevents immediate clogging of the stent.
You can continue your hypertensive drugs on the morning of the day of the procedure. You need to stop certain antidiabetic drugs (METFORMIN) during the day of the procedure and should not be restarted until your doctor told you to do so. Anticoagulants like warfarin need to be stopped.
PROCEDURE
You will change into a hospital gown.
Your sister will insert An intravenous (IV) line
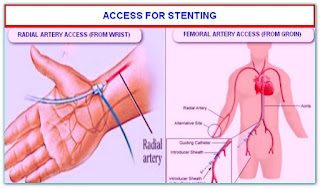
Your doctor will decide whether the radial (wrist) or femoral (groin) access site will be used for the test.
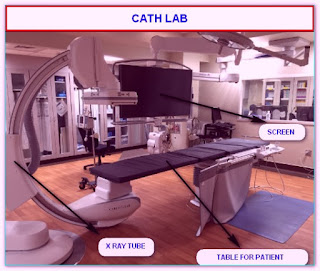
You will go to the catheterization lab (Cath lab) for the stenting.
You will lie on an x-ray table.
You will be connected to a heart monitor.
The doctor will clean the area chosen for the angiogram with a cleaning solution.
Do not touch this area once it is cleaned.
A sterile (germ-free) drape will be placed over you to keep the area clean.
Cardiologists will inject a local anesthetic (freezing) into the groin area or wrist area (radial
artery).
Once the area is frozen (became numb), the cardiologist will insert a sheath (like a large IV)
into the artery.
Through this sheath, the cardiologist will guide small catheters (wires) into the beginning
of heart vessels.
Small amounts of dye will be injected through these catheters to see the heart vessels in the x ray monitor (called a fluoroscope). A wire will be passed across the narrowing and parked distally. Balloon dilatation (passed over the wire and dilates across narrowing) may be necessary in some cases based on the discretion of the doctor. Balloon dilatation will make a way for the stent. A stent (an expandable metal tube usually made of wire mesh) is passed through these catheters to the area of narrowing over the wire. Using X-ray pictures as guidance. Stent is opened (deployed) to keep the artery wide. Stent reduce the risk of narrowing in the future.
This whole procedure usually takes between half an hour to two hours. Sometimes it can be technically difficult and take much longer.
Rarely, a stent is not able to be placed (difficulty due to various reasons), and the procedure is stopped after dilating the narrowed area with a balloon alone. However, the opened artery may close gradually in the future in the majority of such patients.
WHEN WILL BE STENTING DIFFICULT?
Some vessels that are very small and tortuous, have longstanding total blockages (more than 3 months), or have a very amount of calcium in the (hardened) lesion, are more difficult to open with a stent. You may need special gadgets apart from routine to make stenting successful.
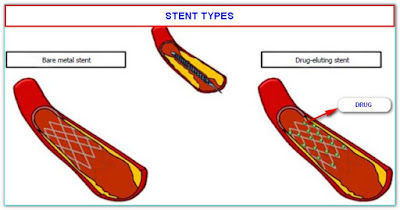
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN BARE-METAL STENT AND DRUG-COATED STENT?
If it is not coated with any medication, it is called a bare-metal stent (BMS). However, they tend to get narrowed (due to the development of excessive tissue growth) in 10-20% of the case (sometimes up to 40%) within one year. Some stents are coated with a
medication that prevents the development of excessive tissue growth and has fewer chances of closure (4-10%), a decrease of more than 70 times. These stents are called “drug-eluting stents.
medication that prevents the development of excessive tissue growth and has fewer chances of closure (4-10%), a decrease of more than 70 times. These stents are called “drug-eluting stents.
IS STENTING COMPLETELY SAFE?
Most people do make a straightforward recovery without any complication. Stenting is an invasive procedure. Hence it carries
some inherent risk of invasive procedure. However, Complications from stenting are relatively infrequent when compared to bypass surgery. The most common complications include discomfort and bleeding at the puncture site (groin or wrist) where the
catheter was inserted.
Small tear (dissection) can develop during dilating heart vessel with balloon or stent. Usually, these tears are small and heals by itself. In some cases, the tear may be large that can cause blockage in blood flow to heart muscle or blood can leak around the heart. This can be life threatening and may cause heart attack or death. Immediate treatment should be given. This usually includes putting in a stent across the tear. Very rarely, such tears may need urgent bypass surgery.
Other complications are perforation of coronary arteries, kidney failure, brain stroke
CAN I HAVE PAIN IN THE FUTURE AFTER STENTING?
Stenting is an effective treatment for majority of people. However, a few people may not get a long-lasting benefit. There is
always some risk of recurrence of symptoms
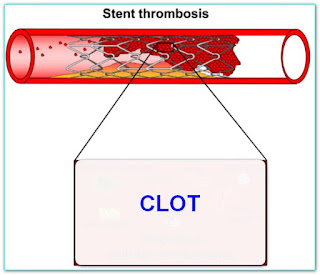
This is often due to recurrent narrowing (restenosis) of the artery at the site of stenting which usually occurs within six months to one year or further narrowing at a separate site (new block). Rarely, your stent may be closed suddenly with a large clot (stent
thrombosis) causing a fresh heart attack. Formation of this clot can be prevented in majority of the patients with blood thinners. Hence, it is mandatory to continue two blood thinner for minimum duration that varies from stent to stent and patient to patient. A minimum of 1 year is recommended in majority.
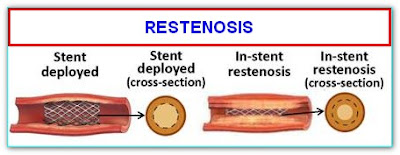
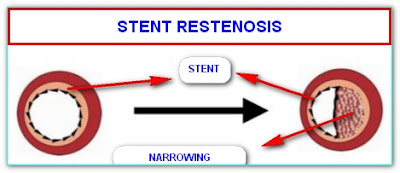
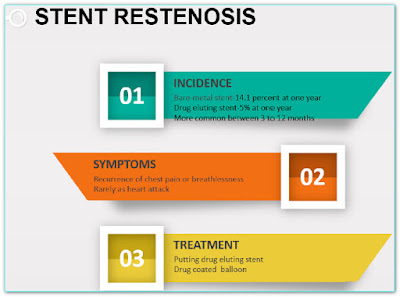
WHAT ARE THE CHANCES OF RECURRENT NARROWING (RESTENOSIS) OF THE ARTERY AT THE SITE OF OPENED ARTERY?
Opened artery tends to get narrowed due to development of excessive tissue growth. This is known as restenosis.
Restenosis that is severe enough to cause symptoms depends on multiple factors that include type of stent, character of the narrowed artery, and character of the patient.
Around 30 percent of people who have the procedure to open a blocked artery without stent placement will develop restenosis usually within 6 months.
Approximately 15 percent of people who have a bare metal stent have restenosis, majority within 6 months to one year.
Less than 10 percent of people who have a drug-coated stent (called drug-eluting stent) develop restenosis which is usually beyond one year. however, these stent have highest chances of closure due to sudden development of fresh clot (stent thrombosis which is a more serious problem than restenosis), hence use of two blood thinners should be strictly followed
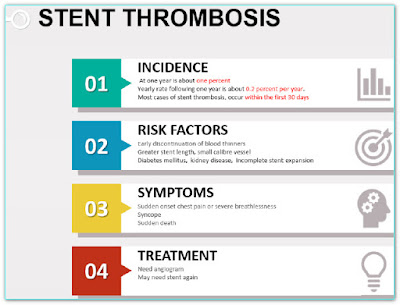
INCREASED CHANCES OF RESTENOSIS OCCURS IN THOSE WITH:
- Diabetes
- Uncontrolled blood pressure
- Continued cigarette smoking
- Arteries that are diffusely narrowed
- High level of bad (LDL) cholesterol
- Stenting is at or near the beginning of a side branch.
- Putting multiple stents in same blood vessel
- Stents that have been placed in a vein (SVG) that was grafted onto the heart during bypass surgery.
CARE AFTER THE PROCEDURE
- Most patients will remain in the hospital for one or two days after stenting.
- Most patients are able to walk on the day after the procedure
ANTIPLATELET MEDICATIONS
Few patients develop a blood clot (thrombosis) inside the stent. This is a serious complication that can cause heart attack which is
sometimes massive or even sudden death. This is called stent thrombosis. It is the metallic nature of the stent that has a tendency to clot during contact with components of blood. A person with stent thrombosis will have chest pain that occurs all of a sudden, severe in nature, present even at rest, and not goes away with sublingual nitrates
Stent thrombosis can occur at any time, even immediately after stenting. Stent thrombosis is divided based on how long it occurred. It may occur within 24 hours, 30 days, or as late as one year or more after stent placement. However, most episodes occur within 30 days.
However, stent thrombosis is a rare complication because blood thinners that prevent clotting are given before and after stent placement for everyone. It is vital that these medications never be discontinued, even for a short time, without the approval of your cardiologist. Never run out of your medicine. If you are not affordable, tell your doctor. He may find a way.
WHEN TO SEEK HELP?
It is vital that you need to seek immediate medical assistance if you experience any of these symptoms that include:
- Sudden onset of Chest pain which is not relieved with one dose of sublingual (under the tongue) nitro-glycerine.
- Sudden swelling of the puncture site
- Severe pain at the puncture site
- Bleeding from the puncture hole
- Drainage of pus from puncture hole.
- High-grade fever
WHAT ARE THE MEASURES SHOULD I TAKE TO SLOW OR REVERSE HEART DISEASE
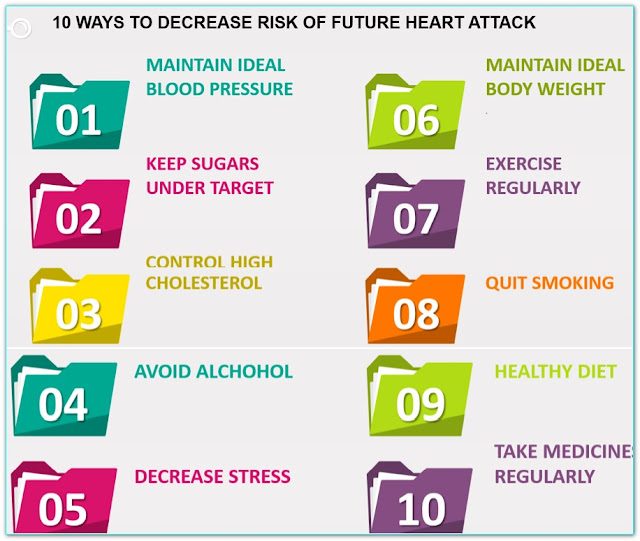
In all patients who underwent stenting, it is important to follow guidelines to reduce the risk of worsening heart disease. These include the following:
- Treat high blood pressure
- Treat high cholesterol
- Treat diabetes
- Quit smoking
- Lose excess weight
- Reduce stress
- Exercise regularly
- Moderation of alcohol intake or avoid drinking
- Healthy dietary habits
- Take medication regularly



I recently found many useful information in your website especially this blog page. Among the lots of comments on your articles. Thanks for sharing. Heartfort supplement
Dr.Mir Jwad Zar khan leading Best orthopedic senior Doctor in Hyderabad at Germanten Hospital,
Looking for knee & Hip replacement Surgeries book an appointment with Dr Mir Jawad Zar khan.
Your article contains very much information . Your article is very informative and useful to know . Thank you so much for sharing this article here. Archbold Medical Center
I found this blog informative or very useful for me. I suggest everyone, once you should go through this.
डबल म्यूटेंट वेरिएंट
This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
I found this blog informative or very useful for me. I suggest everyone, once you should go through this.
Covid-19 vaccine
There are many blogs I have read. But when I read Your Blogs I have found such useful information, fresh content with such amazing editing everything is superb in your blog. Thank you so much for sharing this useful and informative information with us.
order medicine online in jaipur
Such a nice blog with the reference links. Thanks for sharing with others.
Selenium Course In Chennai
Selenium Training Online
Selenium Course In Bangalore
Superb blog post! And this blog clearly explain about for useful information. I would Thanks for sharing this wonderful content. Its very useful to us. Keep it up!
advanced php interview questions
php developer interview questions
php technical interview questions
php interview questions and answers for experienced
Wonderful Blog, thanks for sharing this blog with us, waiting for your next update.
what is machine learning?
why is machine learning important?
Thanks for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your further write ups thanks once again.
nephrology hospital in cuddalore
best heart surgery hospital in cuddalore
Your blog is very valuable which you have shared here about Hip replacement in Bakersfield CA I appreciate your efforts which you have put into this article and also it is a gainful article for us. Thank you for sharing this article here
I've just got PCI stent 3 weeks ago for LAD after a heart attack and now feel better, thank you so much for helpful information
The King Casino: The New King & The World of Gaming
The King 온라인 카지노 Casino is https://febcasino.com/review/merit-casino/ the new place where the real money gambling https://jancasino.com/review/merit-casino/ is legal in Florida and Pennsylvania. We love the https://vannienailor4166blog.blogspot.com/ new jancasino카지노 casino. We've got some great